
Consider this: You’re browsing through an app store, overwhelmed by numerous options. You download an app that looks promising, but within minutes of using it, you feel frustrated by its clunky interface. You uninstall it and move on, never looking back. Now, flip the script. What if that app had been crafted with a deep understanding of your needs, providing a pleasant experience and anticipating and enhancing your journey at every step? You’d not only keep the app but become a loyal user and an advocate.
This is the power of growth design. It’s about creating more than just a product—it’s about building an ecosystem that nurtures and expands your user base. Over the next few sections, we’ll dive into the five principles that can transform your UX design into a robust growth strategy. From understanding your users deeply to leveraging data-driven insights, we’ll explore how you can craft experiences that do more than satisfy—they delight, engage, and grow.
Welcome to the evolution from UX to growth design. Ready to multiply your value? Let’s dive in.
Principle 1 – User-Centric Approach
In the realm of digital design, the user is king. A user-centric approach places the user’s needs, preferences, and behaviors at the forefront of the design process. This principle is the foundation of creating products that not only meet but exceed user expectations, fostering loyalty and driving growth.
The Importance of a User-Centric Approach
Why is a user-centric approach so crucial? Simply put, it ensures that the product resonates with its intended audience. When users feel understood and valued, they are more likely to engage deeply with the product, leading to higher satisfaction and retention rates. By focusing on real user needs rather than assumptions, businesses can create solutions that solve actual problems, enhancing usability and fostering positive user experiences.
Key Elements of a User-Centric Approach
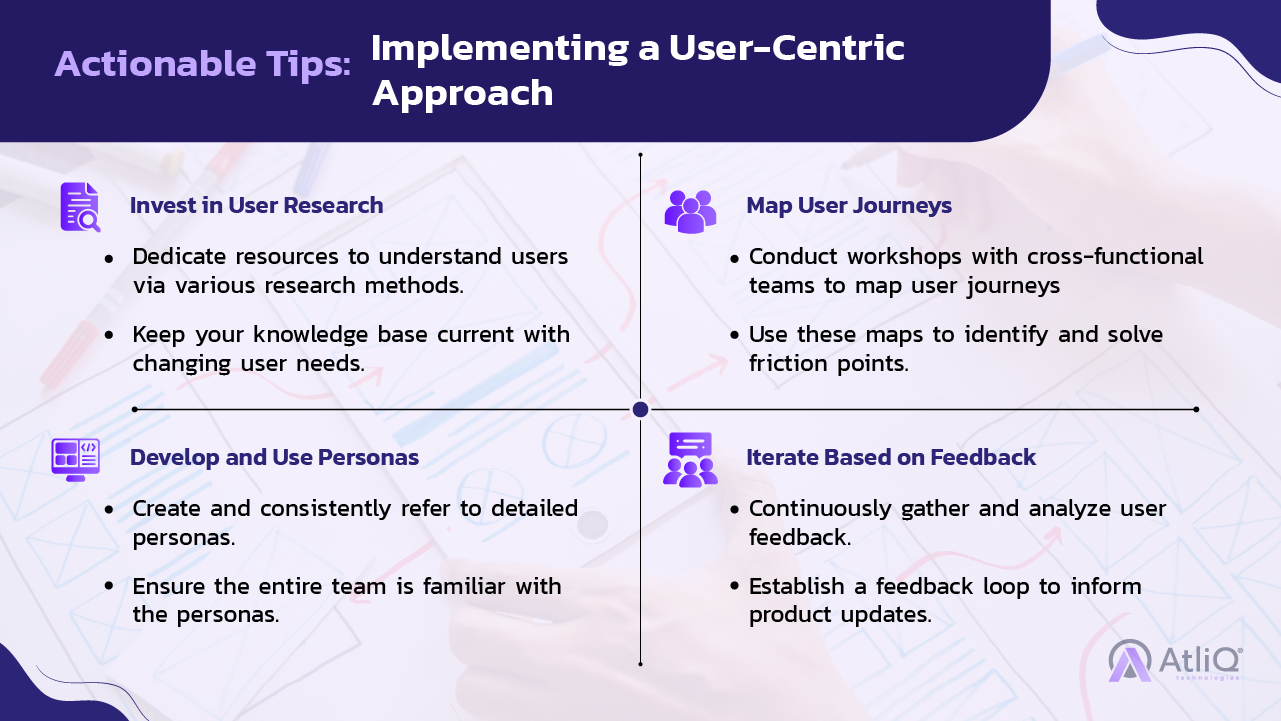
User Research
- Definition: Gathering insights directly from users about their needs, behaviors, and pain points.
- Methods: Surveys, interviews, focus groups, and usability testing.
- Outcome: A deep understanding of the target audience, providing a solid foundation for design decisions.
Persona Development
- Definition: Creating detailed profiles of typical users based on research data.
- Components: Demographics, goals, challenges, and behavioral patterns.
- Outcome: Personas help designers empathize with users and keep their needs in focus throughout the design process.
User Journey Mapping
- Definition: Visualizing the steps users take to achieve a goal with the product.
- Components: Touchpoints, actions, emotions, pain points, and opportunities.
- Outcome: A comprehensive view of the user experience, identifying areas for improvement and innovation.
Case Studies of Successful User-Centric Designs
Spotify
- Context: Struggling with user engagement and retention in its early days.
- Approach: Conducted extensive user research to understand how people discover and listen to music.
- Result: Introduced features like Discover Weekly and personalized playlists, significantly enhancing user satisfaction and engagement.
Airbnb
- Context: Needed to improve the booking experience to compete with traditional hotels.
- Approach: Mapped user journeys and identified pain points in the booking process.
- Result: Simplified the interface and added user reviews, leading to a smoother and more trustworthy booking experience.
Principle 2 – Data-Driven Design
In the fast-paced world of digital products, gut feelings, and intuition can only take you so far. To create designs that truly resonate with users and drive growth, it’s crucial to leverage data at every step. Data-driven design is about making informed decisions based on empirical evidence, ensuring that your design choices are aligned with user needs and behaviors.
Explanation: The Role of Data in Design
The data-driven design shifts the focus from subjective opinions to objective insights. By relying on data, designers can validate hypotheses, measure the impact of their decisions, and continuously optimize the user experience. This approach minimizes guesswork and maximizes the chances of creating a product that not only looks good but also performs exceptionally well.
Key Elements of Data-Driven Design
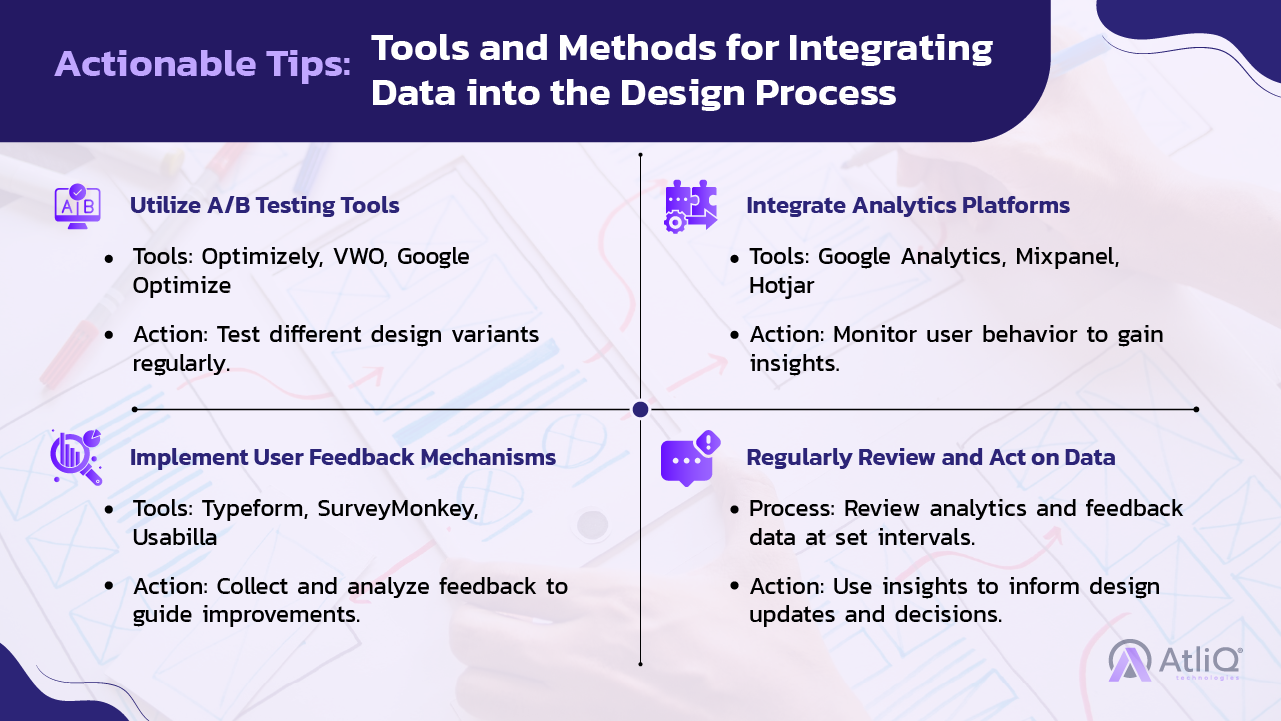
A/B Testing
- Definition: Comparing two versions of a design to see which performs better.
- Process: Split your audience into two groups, present each group with a different design variant, and analyze the results.
- Outcome: Clear evidence on which design elements drive user engagement and conversions.
User Feedback Loops
- Definition: Regularly collecting feedback from users to inform design decisions.
- Methods: Surveys, user interviews, usability testing, and in-app feedback tools.
- Outcome: Continuous insights into user preferences and pain points, enabling iterative improvements.
Analytics Integration
- Definition: Using analytics tools to track user behavior and interactions with your product.
- Tools: Google Analytics, Mixpanel, Hotjar, and other analytics platforms.
- Outcome: Detailed understanding of how users navigate your product, identifying areas for optimization and enhancement.
Examples: Companies Successfully Utilizing Data-Driven Design
Netflix
- Context: Needed to enhance user engagement and retention.
- Approach: Implemented extensive A/B testing to optimize everything from homepage layouts to recommendation algorithms.
- Result: Increased user engagement and retention rates, contributing to their global success.
Amazon
- Context: Aiming to improve the shopping experience.
- Approach: Integrated robust analytics and user feedback mechanisms to continuously refine their website and app design.
- Result: A seamless, highly personalized shopping experience that boosts conversions and customer satisfaction.
Principle 3 – Seamless User Experience
Creating a seamless and intuitive user experience (UX) is paramount in today’s digital landscape. A smooth UX enhances user satisfaction and drives engagement, retention, and ultimately, growth. When users can navigate your product effortlessly, they are more likely to interact positively, which translates into better business outcomes.
Explanation: The Importance of a Seamless User Experience
A seamless user experience eliminates friction, making it easy for users to achieve their goals without frustration. This approach prioritizes clarity, simplicity, and efficiency, ensuring that every interaction feels natural and intuitive. A great UX is often invisible—it just works. By focusing on creating a smooth experience, you build trust and loyalty with your users, which are crucial for sustained growth.
Key Elements of a Seamless User Experience
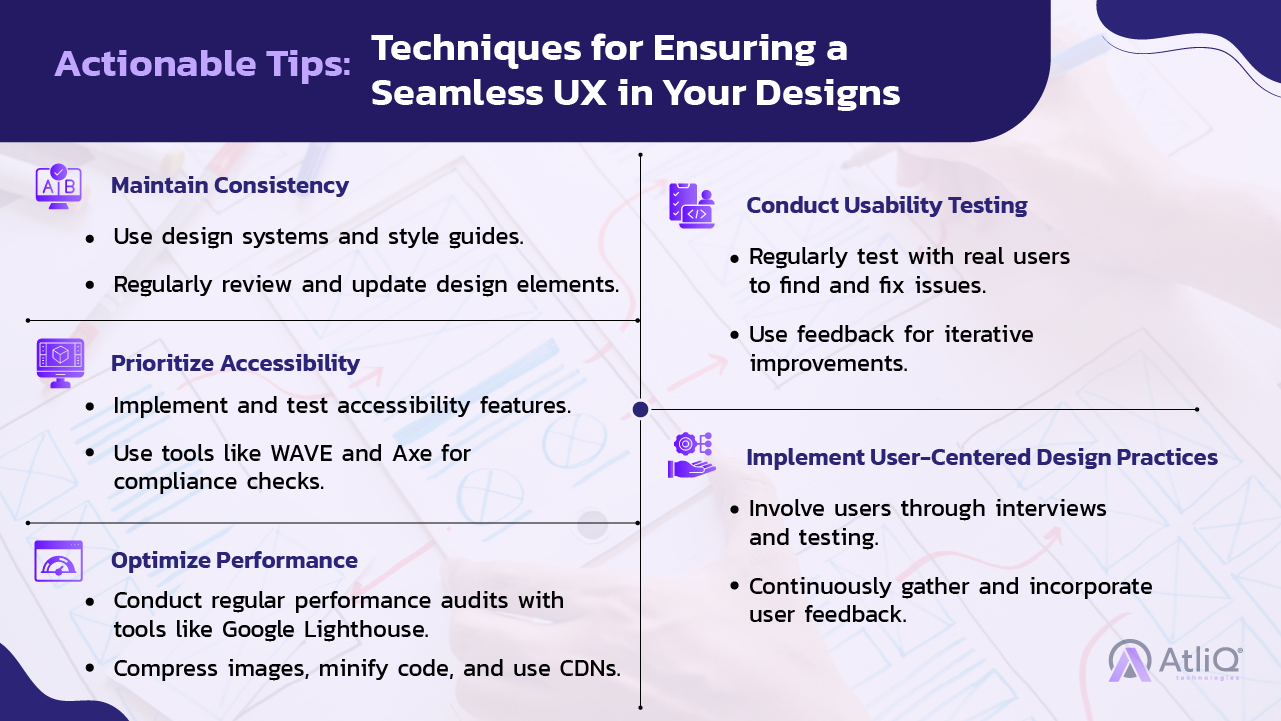
Consistency
- Definition: Maintaining uniform design elements and interactions across all parts of the product.
- Importance: Helps users predict and understand how the product works, reducing cognitive load and increasing comfort.
- Implementation: Use consistent visual styles, language, and interaction patterns.
Accessibility
- Definition: Designing products that are usable by people with diverse abilities.
- Importance: Ensures inclusivity and expands your user base.
- Implementation: Follow accessibility guidelines (e.g., WCAG), provide alternative text for images, ensure keyboard navigability, and use high-contrast color schemes.
Performance Optimization
- Definition: Ensuring that your product loads quickly and runs smoothly.
- Importance: Improves user satisfaction by reducing waiting times and preventing frustration.
- Implementation: Optimize images and code, use content delivery networks (CDNs), and minimize server response times.
Examples: Products with Exceptional User Experiences
Apple
- Context: Known for its intuitive and consistent design across all products.
- Approach: Focuses on simplicity and user-centered design.
- Result: Products like the iPhone and MacBook are celebrated for their ease of use and seamless experience.
Slack
- Context: Aiming to provide a frictionless communication platform.
- Approach: Prioritized performance and accessibility, ensuring a smooth experience on various devices.
- Result: Widely adopted and praised for its user-friendly interface and reliable performance.
Principle 4 – Scalable Design Systems
Maintaining a consistent and efficient design becomes increasingly challenging as your digital product grows. Scalable design systems provide the structure and flexibility needed to support this growth, ensuring your product remains cohesive and adaptable across various platforms and devices.
Explanation: The Need for Scalable Design Systems
A scalable design system allows for efficient collaboration among design and development teams, reduces redundancy, and ensures consistency across all touchpoints. By establishing a unified set of guidelines, components, and tools, scalable design systems streamline the design process, making it easier to implement updates and expand your product. This approach saves time and resources and enhances the overall user experience by maintaining a consistent look and feel.
Key Elements of Scalable Design Systems
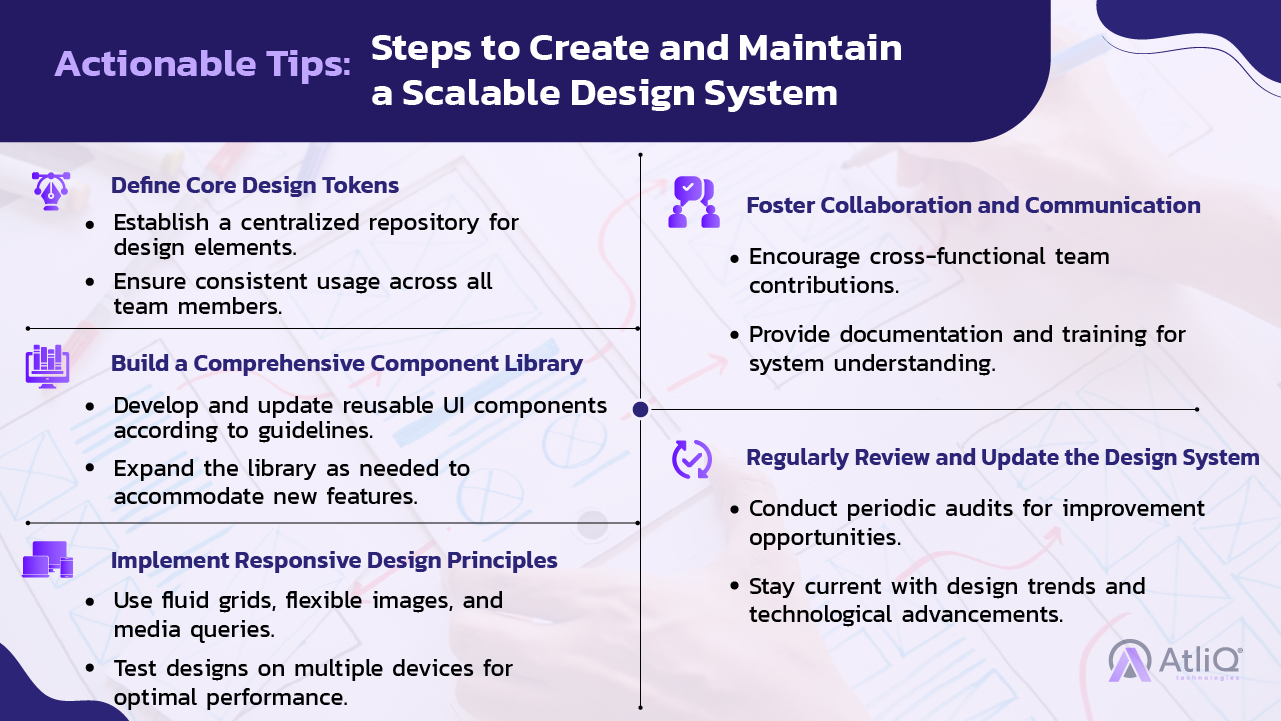
Design Tokens
- Definition: Basic elements such as colors, typography, and spacing are used throughout the design system.
- Importance: Ensure consistency and flexibility by defining core design properties that can be easily updated and applied across different components.
- Implementation: Centralize design tokens in a shared repository and use them across all design and development tools.
Component Libraries
- Definition: Collections of reusable UI components that adhere to the design guidelines.
- Importance: Streamline development by providing pre-built, standardized components that can be easily integrated into various products.
- Implementation: Develop and maintain a comprehensive component library accessible to all team members.
Responsive Design
- Definition: Designing products that provide an optimal viewing experience across various devices and screen sizes.
- Importance: Ensure your product is accessible and functional on all devices, enhancing the user experience.
- Implementation: Create a responsive design framework using fluid grids, flexible images, and media queries.
Examples: Brands with Scalable Design Systems
- Context: Needed a unified design system to maintain consistency across its vast array of products.
- Approach: Developed the Material Design system, which includes design tokens, component libraries, and guidelines for responsive design.
- Result: Achieved a cohesive user experience across all Google products, making navigating and interacting with different services easier for users.
Atlassian
- Context: Aiming to streamline design and development processes across its suite of collaboration tools.
- Approach: Created the Atlassian Design System, which provides comprehensive guidelines, reusable components, and design tokens.
- Result: Improved efficiency in product development and ensured a consistent user experience across all Atlassian products.
Principle 5 – Continuous Improvement and Iteration
In the dynamic landscape of digital product development, the journey doesn’t end with the initial launch—it’s an ongoing process of refinement and evolution. Principle 5 emphasizes the importance of continuous improvement and iteration in design. By embracing this principle, you can stay ahead of the curve, respond to user needs more effectively, and drive sustained growth for your product.
Explanation: The Importance of Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is more than just a buzzword—it’s a mindset that fosters innovation and excellence. By constantly refining and iterating your design, you can adapt to changing market conditions, address user feedback, and seize new opportunities. This approach ensures that your product remains relevant, competitive, and valuable to users over time.
Key Elements of Continuous Improvement
Agile Methodologies
- Definition: An iterative approach to software development that emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and customer feedback.
- Importance: Enables teams to respond quickly to changing requirements and deliver incremental improvements to the product.
- Implementation: Adopt agile frameworks like Scrum or Kanban and prioritize iterative development cycles.
User Feedback Integration
- Definition: Incorporating feedback from users into the design and development process.
- Importance: Provides valuable insights into user preferences, pain points, and needs, guiding design decisions.
- Implementation: Use feedback channels such as surveys, user interviews, and analytics to gather and analyze user input.
Regular Updates and Testing
- Definition: Releasing updates to the product regularly and testing them rigorously.
- Importance: Ensures product remains stable, secure, and aligned with user expectations.
- Implementation: Establish a schedule for regular updates and conduct thorough testing before each release.
Examples: How Continuous Improvement Drives Growth
- Context: Constantly evolves its platform based on user feedback and market trends.
- Approach: Regularly introduces new features and updates, often in response to user demand.
- Result: Maintains high user engagement and attracts new users, driving sustained growth and profitability.
Tesla
- Context: Known for its innovative approach to product development and continuous improvement.
- Approach: Releases over-the-air software updates to improve vehicle performance, add new features, and address issues.
- Result: Enhances customer satisfaction, generates positive publicity, and maintains a competitive edge in the market.

In the ever-evolving landscape of digital design, the journey from UX to growth design is a transformational one. By embracing the five principles outlined in this blog—putting the user at the center, leveraging data-driven insights, crafting a seamless user experience, establishing scalable design systems, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement—you can unlock the full potential of your digital product and multiply its value.
As you embark on this journey, remember that it’s not just about creating a product—it’s about building an experience, an ecosystem that delights users, fosters loyalty, and drives sustainable growth. By applying these principles with diligence and creativity, you can transform your design process and propel your product to new heights of success.
So, are you ready to embark on the journey from UX to growth designs? Let’s create experiences that not only meet but exceed expectations, delighting users and multiplying value along the way.
The possibilities are endless, and the journey is just beginning.